Question 1 of 15
X and Y are the reactants in a chemical reaction for which E is the enzyme. The product is Z.
The first three stages in the reaction are shown.
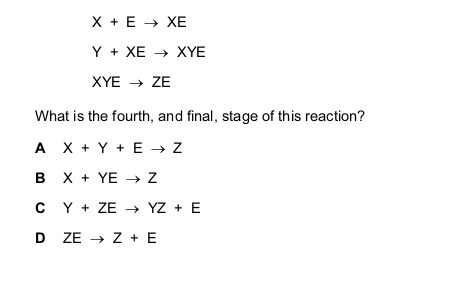
This Enzyme Quiz 1 quiz contains 15 multiple choice questions designed to help you revise and test your Enzyme Quiz knowledge. Select an answer for each question and click “Submit Answer” to see instant feedback. Take your time and try to score as high as possible!
Here, we will be looking at Enzymes and this is the first part, quiz 1 on enzymes. Note that the body is large and complex and most chemical reactions occur in the body. These chemical reactions are slow so much so that they are aided by biological catalysts to go through quickly to completion. These biological catalysts are enzymes and they also play a key role in the sustainable development of society because they also play a central role in the chemistry of nature. In the course of this quiz, you will learn how enzymes function and act. These quizzes give opportunities to students to study such quizzes anywhere at their convenient time and the quizzes are also free.
An enzyme is a biological catalyst protein in nature and helps to speed up the rate of a specific Biochemical reaction in the cell of the body. These enzymes are not destroyed during the reaction and are used over and over again, unchanged. There are few types of enzymes, these are
Enzyme action: Enzymes function by binding themselves to substances known as substrates, that is
This summary will help boost your thirst for more knowledge on this topic. Take the quiz and you will learn, even more, you will be answering 15 MCQs with a chance of 1 out of 4 to have the correct answer, so are you up to the task? Let’s find out.
Best Luck!!
Question 1 of 15
X and Y are the reactants in a chemical reaction for which E is the enzyme. The product is Z.
The first three stages in the reaction are shown.
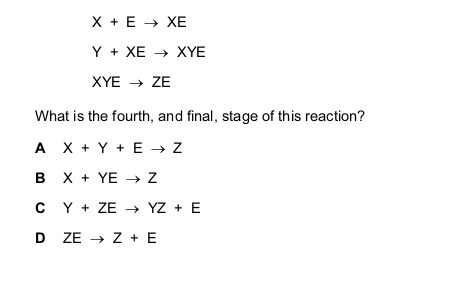
Question 2 of 15
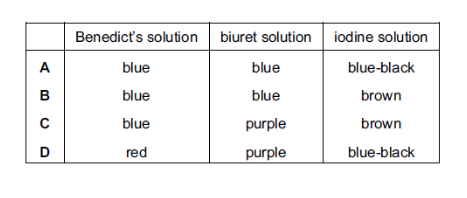
Amylase solution is tested with Benedict’s solution, biuret solution and iodine solution.
Which colours are obtained?
Question 3 of 15
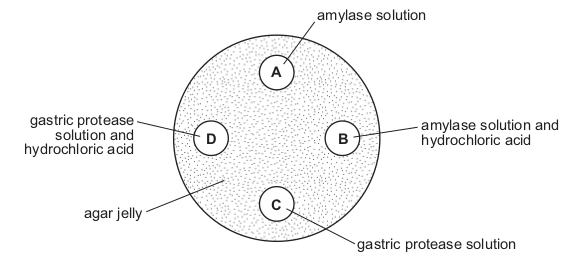
A dish is filled with agar jelly containing starch. Four holes are cut in the jelly and each hole is
filled as shown.
After 30 minutes, which hole will be surrounded by the largest area without starch?
Question 4 of 15
Some organisms live at the bottom of the seas where it is very dark. To synthesise glucose, they
use energy from chemicals in the very hot water that comes out of volcanoes.
Question 5 of 15
Five tubes containing cooked egg-white are set up as shown. Protease solutions of different pH are added to each tube.
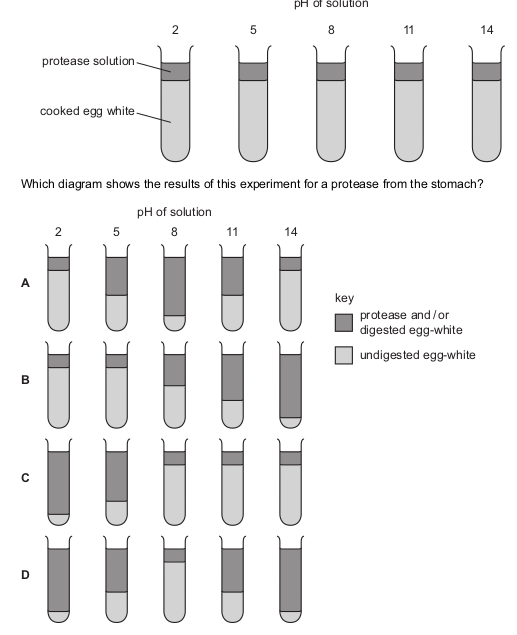
Question 6 of 15
What is the enzyme that controls a reaction in which both the enzyme and the substrate can
denature at high temperatures?
Question 7 of 15
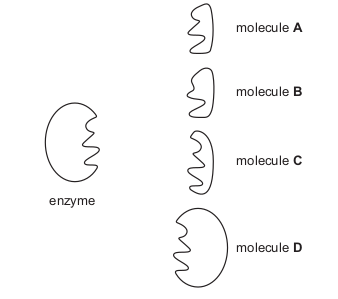
The diagram represents an enzyme and four molecules, A, B, C and D.
Which molecule is the substrate of this enzyme?
Question 8 of 15
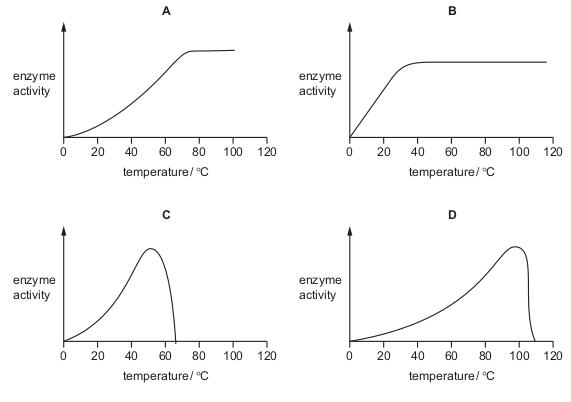
A bacterium lives in hot springs at temperatures of 75 °C to 85 °C. Which
graph represents the activity of enzymes found in these bacteria?
Question 9 of 15
The diagram represents the ‘lock and key’ mechanism of an enzyme that works best at pH 7.
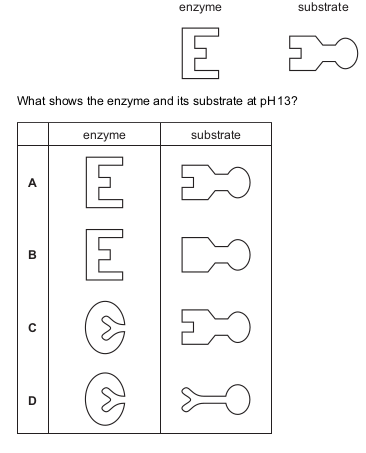
Question 10 of 15
The diagram represents how an enzyme molecule changes in shape.
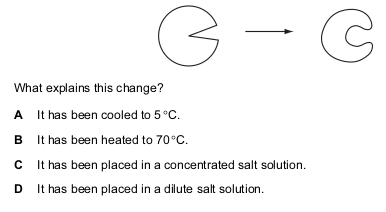
Question 11 of 15
Which statements are correct for all enzymes?
1 They are proteins.
2 They are secreted into the alimentary canal.
3 They speed up biochemical reactions.
4 None of them work at low pH.
Question 12 of 15
In an enzyme action, where is the active site and where are the lock and the key?
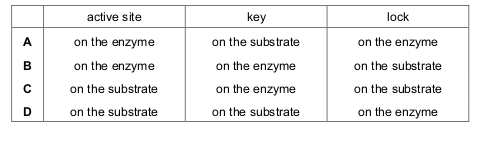
Question 13 of 15
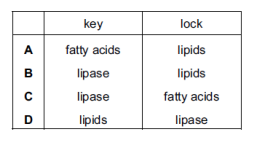
Starch is digested to maltose by the enzyme amylase.
According to the ‘lock and key’ hypothesis, which is the ‘key’ and which is the ‘lock’?
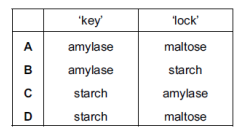
Question 14 of 15
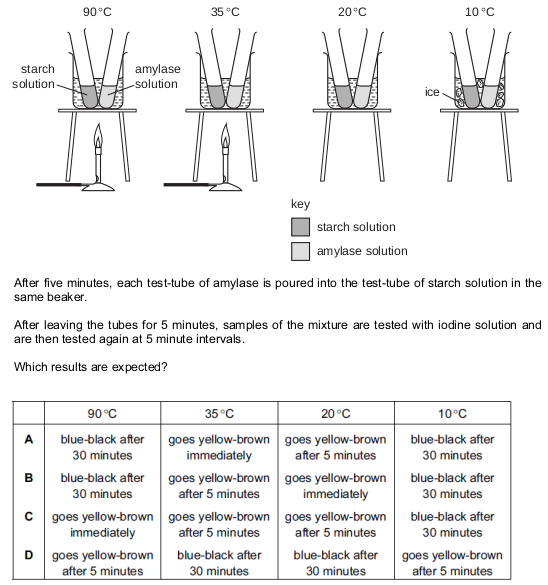
The diagram shows an experiment on amylase.
Each beaker contains water at the temperature shown.
Question 15 of 15
According to the lock and key hypothesis, which is the lock and which is the key for the enzyme
lipase?