Extraction of Metals Quiz
17 QuestionsQuiz Description
The extraction of metals in chemistry is simply the process by which metals are gotten from their ores buried deep under the ground. The metal deposits are known as metal ores which are in varying abundances in the crust of the Earth. The metal ore is always very different from the finished metals that we see in bridges and buildings.
The extraction of metals plays a very vital role in every civilisation in that the extracted metals are used to make coins, farming tools, weapons for war, building tools and even used in the construction of buildings. These metals have changed the lives of millions over the world.
Have you learned enough about Metals ? Are you confident enough to answer the quiz? To view other quizzes in gcse chemistry Click here.
Good luck
Which of these metals should react with dilute hydrochloric acid, but very slowly?

Which metal is less reactive than sodium but must be extracted using electrolysis of the molten ore?
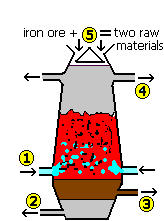
Stages in the extraction of iron in a blast furnace are described below after iron ore, coke and limestone have been added at the top, but not in the correct order. (1) carbon dioxide reacts with coke (carbon) to form carbon monoxide (2) limestone combines with acid impurities (3) hot air is blown into the furnace (4) carbon monoxide reacts with iron oxide to make iron (5) coke (carbon) burns to form carbon dioxide Which is the correct order of sequence for (1) to (5)?
The reactions in the blast furnace to produce iron are summarised by equations (1) to (4). The symbol equations may NOT be numerically balanced.
... (1) C + O2 ==> CO2
... (2) CO2 + C ==> CO
... (3) Fe2O3 + CO ==> Fe + CO2
... (4) CaCO3 + SiO2 ==> CaSiO3 + CO2
Which statement is TRUE?
Ingots of aluminium from its electrolytic extraction can be stored outside in all weathers. Why do aluminium ingots not corrode away, despite aluminium being quite high in the reactivity series of metals?
Which removes impurities from iron in the blast furnace extraction of iron?
The reactions in the blast furnace to produce iron are summarised by equations (1) to (4). The symbol equations may NOT be numerically balanced.
... (1) C + O2 ==> CO2
... (2) CO2 + C ==> CO
... (3) Fe2O3 + CO ==> Fe + CO2
... (4) CaCO3 + SiO2 ==> CaSiO3 + CO2
Which statement is TRUE?