Energy Transfer in Physical and Chemical Changes Quiz
15 QuestionsQuiz Description
This particular quiz guides students on the fundamentals of the energy transfer that is accompanied by a physical or a chemical change. Composed of questions with four options of which one is correct. Questions which have been set based on the national curriculum for the gcse and questions that meet up to the examination standards
As we all know, a physical change changes only the appearance of a particular substance with no new substance formed whereas a chemical change causes the substance to change its appearance into a totally different substance. The energy transfer that takes place in both a physical and a chemical change is the movement of heat. For a physical change, from the surroundings, heat is absorbed into the system and for a chemical change, the heat is instead released from the system into the surroundings.
` `This quiz is just part of a set of GCSE quizzes for those that wish to go in for the gcse. Go ahead and test your knowledge with the questions below.
Good luck
When an endothermic reaction takes place, the reaction mixture takes in heat because?
Equal amounts of four different substances (A-D) where added separately to equal amounts of an acid and a thermometer placed in the mixture. For which substance is the reaction the most endothermic?
When ammonium chloride dissolves in water the temperature falls. The type of energy change is described as?
Equal amounts of four different substances (A-D) where added separately to equal amounts of an acid and a thermometer placed in the mixture. For which substance is the reaction the most exothermic?
When magnesium dissolves in hydrochloric acid the temperature rises. The type of energy change is described as?
Energy is needed to make a mixture of methane and oxygen react. The mixture explodes when a lighted splint is applied. What type of energy is supplied by the splint?
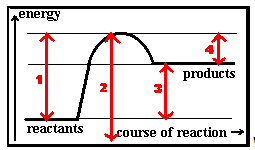
Which of the following energy changes changes corresponds to the overall energy change for the reaction?
Which of these involves a chemical reaction? [et-82] 1. baking bread : 2. boiling water : 3. corroding metals


