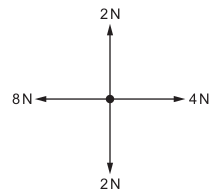
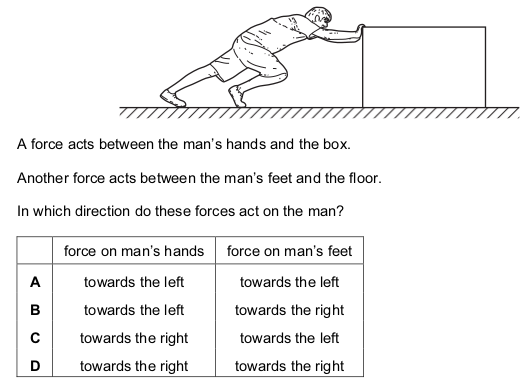
Dynamics Quiz 1
20 QuestionsQuiz Description
This A level physics quiz is all about Dynamics. Here, we are going to cover some important sections of dynamics such as the application of Newton’s third law, calculation of resultant force, etc. In a nutshell, this quiz covers a great section of dynamics, thus, answering the quiz correctly is a guarantee of your success in answering most dynamic questions correctly.
Dynamics is another branch of mechanics, and it is concerned with the study of forces and their relationship with motion and equilibrium. Unlike kinematics, dynamics is further divided into two types: linear and rotational dynamics. Linear dynamics studies the motion of bodies in a straight line, whereas Rotational dynamics studies the motion of bodies in a circular or curved path. We’ve heard of forces, what is a force?
A force is a push or a pull exerted on a body, and there are two categories of forces which are action-at-a-distance force, and contact force.
Dynamics is a very important topic that should be mastered to the fingertips. For this reason, this quiz, and other A level Physics quizzes are available on this platform for you to train yourself to understand better. Wish you the best as you solve the problems!
A man pulls a sledge of mass 25 kg across level ground with a horizontal force of 60 N.
A constant force of friction of 20 N acts on the sledge.
What is the acceleration of the sledge?
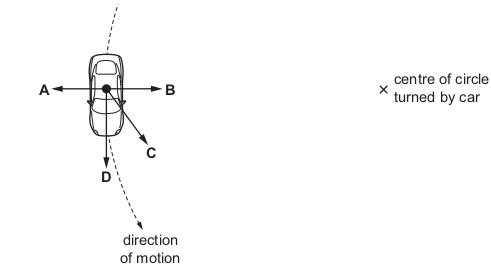
A car moves in a circle at constant speed.
What is the direction of the resultant force acting on the car?
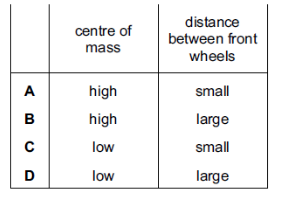
When a car turns a corner at speed, it risks toppling over. Two factors affecting the stability of a car are the height of its centre of mass and the distance between its front wheels.
Which factors make the car most stable?
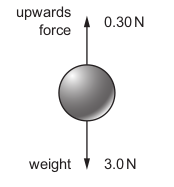
A metal ball of mass 0.30 kg and weight 3.0 N is held so that it is below the surface of oil.
It experiences an upwards force of 0.30 N.
When the ball is released, what is its initial acceleration?
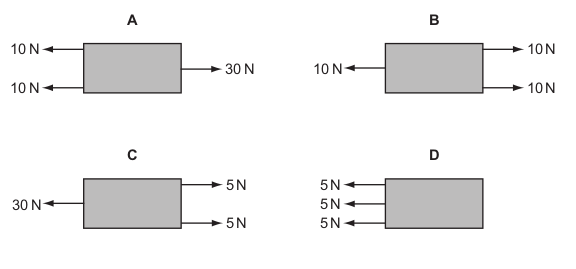
In which example does friction act in the direction of forward motion of the object on which it acts?
An apple of mass 0.15 kg and weight 1.5 N falls from a tree. At one point during its fall, the air resistance on the apple is 0.60 N upwards.
What is the acceleration of the apple at this point?
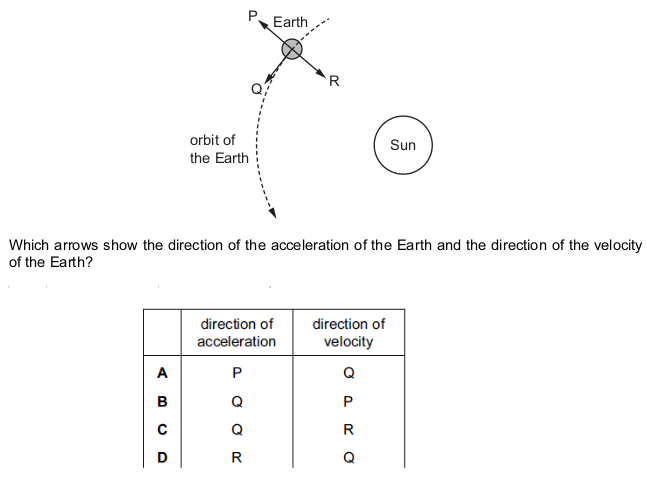
Four of the gravitational forces that act between bodies in the Solar System are described below.
P the force on the Moon due to the Earth
Q the force on the Earth due to the Sun
R the force on the Earth due to the Moon
S the force on the Moon due to the Sun
Which two forces are a Newton’s third law pair (action and reaction)?
A satellite is orbiting the Earth.
What is the direction of the force on the satellite causing this circular motion?
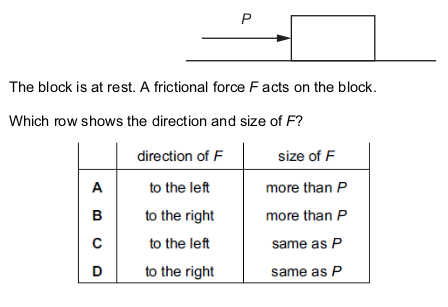
The diagram shows a block of stone on a rough horizontal surface.
Force P acts on the block as shown.
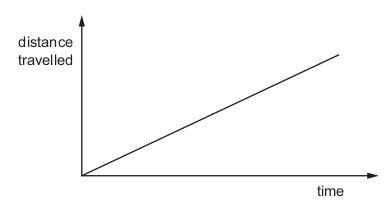
The distance traveled by a car is increasing uniformly as it is driven along a straight road up a hill.
Which quantity for the car is constant but not zero?
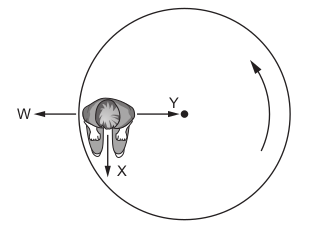
A boy sits on a playground roundabout (carousel). The roundabout carries the boy in a horizontal, anticlockwise circle at a constant speed.
The diagram shows the view of the roundabout from above. What describes the resultant force on the boy?
In a model of an atom, electrons move in circular orbits around a nucleus. Which statement about the electrons is correct?
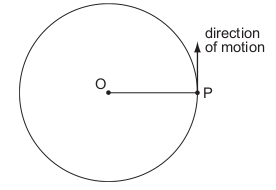
A particle P is moving in a horizontal circle about O. P moves at constant speed. Which statement is true?
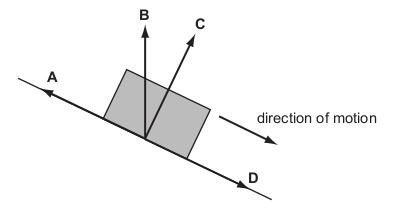
A body slides down a friction-less slope as shown.
As the body presses on the surface, the surface pushes back on the body. The force of the
surface on the body is sometimes called the reaction force.
In which direction does the reaction force act?
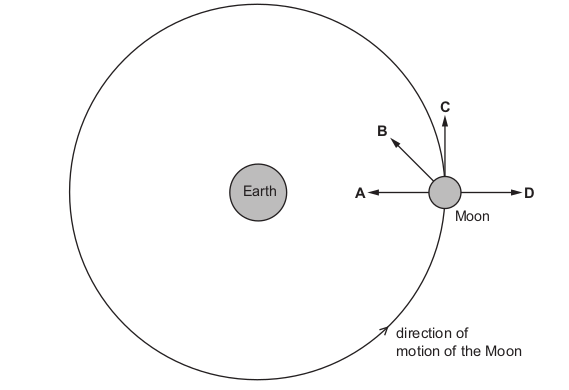
The diagram represents the Moon in its orbit around the Earth.
Which arrow represents the direction of the resultant force acting on the Moon at the instant
shown?