Atomic structure and radioactivity quiz
15 QuestionsQuiz Description
Here in this A level Chemistry quiz, we are going to take a look at atomic structure and radioactivity. Generally, our point of focus is going to be on the calculation of the half-life of a radioactive substance, the identification of the various types of radioactive particles (Alpha, Beta, and Gamma particles), and isotopy. This quiz covers a lot as far as atomic structure and radioactivity is concerned.
Radioactivity (also called radioactive decay) as we know is the process whereby unstable nuclei spontaneously release energy in the form of radiation. Hence, any substance containing unstable nuclei is said to be radioactive. There exist three main types of radioactive decay which are: alpha, beta, and gamma decay.
Alpha decay is said to have occurred when a nucleus sends out an alpha particle (helium nucleus), Beta decay occurs when it emits an electron, and Gamma decay occurs when the nucleus undergoes either alpha or better decay, then the resulting daughter nucleus which is left in an excited state can then decay to a lower energy level emitting a gamma-ray proton.
Radioactivity is a very interesting topic in chemistry that is worth taking a quiz for. If you are willing to have a full understanding of this topic, just answer the quiz and be sure of improving your performance. Good luck as you solve it!
One gram of each of the following chemicals was placed at a distance of 2 cm from a Geiger-Muller tube and counter. The results are given below. The background count was found to be 34 counts/minute. Which chemical has a radioactivity of 18 counts/min?
Radioactive tracers can be used in medicine to help diagnose problems with for example, blood supply, liver and lung function. The patient is injected with an aqueous solution containing a small amount of the radioisotope (in the case of lungs, air containing a little radioactive gas). The location and movement of the tracer can followed by standing the patient against a detection screen. Why is an alpha emitting radioisotope NOT suitable as a tracer?
The half-life of radioactive thorium-234 is 24 days. A sample contains 8g of thorium-234. After how many days will it contain only 0.25g of thorium-24?
The emissions from four different radioactive sources where tested to see which materials would absorb and stop the radiation. The amount of radiation passing through was measured with a Geiger Counter in counts/second (c/s). From the data, which source gives out mainly ALPHA radiation?
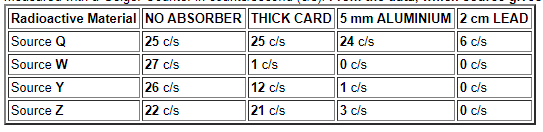
Which of the following radioactive sources would need the greatest thickness of lead to prevent harmful radiation escaping into the environment?
One type of ionising radiation is an alpha particle. Which of the following correctly describes an alpha particle? [rad-33] 1. cannot pass through a sheet of paper : 2. consists of a helium nucleus : 3. has a positive charge
Radioactive tracers can be used to find leaks in pipes underground. The gamma emitter, Iridium-183 (half-life 54 minutes) can be used. Why is iridium-183 a suitable radioactive tracer to use?
The radioactivity due to naturally occurring uranium minerals in rocks contributes to what is known as?
Plutonium-234 is an alpha-emitting radioactive isotope. The radiation it gives out is best described as?
One gram of each of the following chemicals was placed at a distance of 2 cm from a Geiger-Muller tube and counter. The results are given below. The background count was found to be 34 counts/minute. Which chemical is the least radioactive?
The half-life of radioactive thorium-234 is 24 days. A sample contains 8g of thorium-234. After how many days will it contain only 4g of thorium-24?


