A Level Economics Quiz 2018 Part 1
15 QuestionsQuiz Description
One of the main definitions of economics is “the creation, consumption, and transfer of wealth”.
Economics being one of the main social science subjects at the Advanced Level means it has more to offer in the society. In this sense students/individuals must have a vast knowledge about this knowledge. So, in order to help students prepare for the upcoming CGCE examinations, we have put together a quiz which is to help students overcome their challenges during the examination.
This quiz is composed of past CGCE question of the June session of 2018. The quiz is made up of 15 questions with each question having 4 different options. The 15 questions are mainly on the topics of “demand, economic growth, employment etc.”
The purpose of this quiz is to help you (students), build your confidence when going in for the examination and also to help orientate you on the type of questions you might encounter during the examination.
On completion of this quiz, you can then move on to the next.
Good luck!!!
Figures 1 to 4 below show shifts in the production possibilities curve for a given country.
Which of the figures (1, 2, 3 and 4) indicates that the economy is more efficient in the production of good Y?
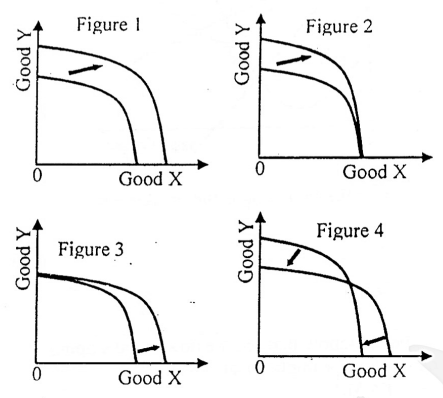
The basis for determining the allocation of factors of production in a market economy is:
An offer of new shares to existing shareholders as a means of raising funds internally is called:
The total amount of capital that a company decides to float for public subscription is:
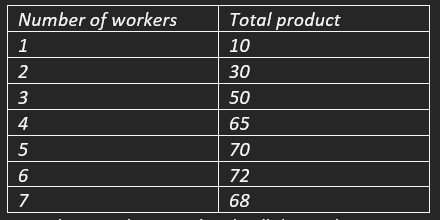
The table shows different output levels produced by different workers
At what employment level will diminishing returns occur?
The average number of daughters that would be born to a female if she passed through her lifetime is described as the:
If a supermarket reduces the price of its soap from 300 FCFA to 200 FCFA and buyers decide to increase their demand from 2,000 cubes to 2,500 cubes, the price elasticity of demand would be:
The price of petroleum products is raised from 570 FCFA to 650 FCFA per litre with
the price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply being 1.5 and 3.5 respectively. How much additional tax per unit will a consumer pay per litre of petrol?
In a normal situation of supply, an increase in the supply of a commodity in the market will lead to:
If the cross-price elasticity of demand between goods A and B is zero, then these goods are:
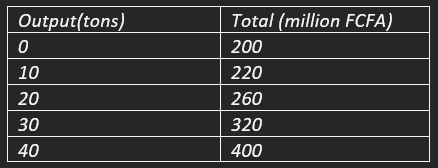
The table refers to the costs of a firm at various levels of output
What is the average fixed cost of producing 40 tons of output?
Which of the following options will a government use to best control the consumption of harmful goods?


